Inflammation Test – CRP
Inflammation Test
A C-Reactive Protein (CRP) test measures the level of CRP in the blood, which rises in response to inflammation. CRP is produced by the liver and released into the bloodstream in response to inflammation or infection. Elevated CRP levels can indicate acute conditions such as bacterial infections, rheumatoid arthritis, or chronic inflammatory diseases like Crohn’s disease. The test helps diagnose conditions causing inflammation, monitor the severity of diseases, and assess treatment effectiveness. While not disease-specific, it is a valuable marker in identifying and managing inflammatory conditions.
Key Indicators Reported: CRP
₹750.00
Only customers holding Indian debit or credit cards may place their order through this portal. International customers are requested to write to us at [email protected] so that we may assist them in placing the order.
General FAQs
Home-to-lab testing allows individuals to collect samples comfortably at home. The main advantages of home sampling include convenience, privacy, and accessibility, as individuals can perform the tests at their own convenience.
Once the sample is collected, it is sent to our laboratory for analysis from anywhere in the world. You will be notified on your registered email once the results are ready, and can be downloaded from your registered account.
DBS testing is no more painful than a self-prick for a glucometer test. The kit contains one-time-use safety lancets which are used for pricking a finger and depositing a sample on a special filter paper card. The blood spot deposited on the filter paper card is allowed to dry, and hence the name dried blood spot.
Similarly, some tests may require saliva, urine or stool samples, which can also be collected on special filter paper cards. This makes the sample collection completely non-invasive.
Watching the instructional video and carefully reading the instruction manual before conducting the test should ensure a smooth experience. Should you encounter any difficulties, please do not hesitate to contact us for assistance.
Once we receive your sample, the average response time is 7-10 business days to receive the results.
Lipomic LifeSciences can provide evidence-based suggestions for lifestyle changes that you can make to positively impact your health. We can also connect you with leading medical experts who can guide and discuss potential next steps.
Test Specific FAQs
The word ‘inflammation’ comes from the Latin word “inflammare” which means ‘to set on fire’. Traditionally, one associates inflammation with the four cardinal signs – redness, swelling, heat and pain. This is what is known as the classical “acute inflammation”. This happens in response to an injury or an infection by a foreign agent like bacteria, virus, fungus, parasites etc. The body’s defence mechanism is activated and cells and molecules reach the site of injury/infection in order to eliminate the offending agents. Thus, inflammation is necessary to control infections, heal wounds and clear injured tissues and festering sores. Generally, inflammation subsides after the aforementioned goals are achieved. What happens however, when the body’s response does not subside and may not even be against any particular target? That is what is known as chronic inflammation. By definition, chronic inflammation is a response of prolonged duration (weeks or months). Causes of chronic inflammation can include persistent infections, hypersensitivity diseases, prolonged exposure to toxic agents etc. Research now links chronic inflammation with stress, poor lifestyle choices and dietary patterns. If left unchecked, prolonged chronic inflammation starts affecting and attacking healthy cells. Chronic inflammation creates a microenvironment suitable to the development of several complex diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, auto-immune diseases.
C-Reactive Protein or CRP is a protein produced primarily by the liver in response to inflammation. The levels of CRP increase up to a 1000 fold at the site of infection or injury. CRP has traditionally been used as a marker for infection and cardiovascular diseases. Baseline CRP levels can vary according to age, gender, smoking status, weight, lipid levels, and blood pressure but for a standard CRP test, less than 3 milligram per liter (mg/L). A test result showing a CRP level greater than 3 mg/L should be further investigated by a medical practitioner.
The test results will indicate whether your CRP levels are in the reference range. CRP is a non specific marker of inflammation and might be temporarily elevated due to a recent infection, illness or trauma and it is recommended that you repeat the CRP test after a month. If your levels are elevated after the retest too, you must share your results with your healthcare provider and discuss potential steps.
Chronic Inflammation is related to a myriad of health problems, as represented in the diagram below:
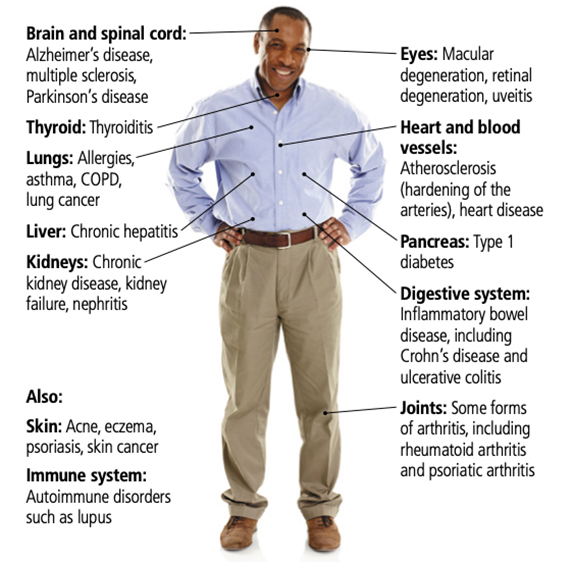
Source: Fighting Inflammation, Harvard Special Health Report
Sample Report
General FAQs
Home-to-lab testing allows individuals to collect samples comfortably at home. The main advantages of home sampling include convenience, privacy, and accessibility, as individuals can perform the tests at their own convenience.
Once the sample is collected, it is sent to our laboratory for analysis from anywhere in the world. You will be notified on your registered email once the results are ready, and can be downloaded from your registered account.
DBS testing is no more painful than a self-prick for a glucometer test. The kit contains one-time-use safety lancets which are used for pricking a finger and depositing a sample on a special filter paper card. The blood spot deposited on the filter paper card is allowed to dry, and hence the name dried blood spot.
Similarly, some tests may require saliva, urine or stool samples, which can also be collected on special filter paper cards. This makes the sample collection completely non-invasive.
Watching the instructional video and carefully reading the instruction manual before conducting the test should ensure a smooth experience. Should you encounter any difficulties, please do not hesitate to contact us for assistance.
Once we receive your sample, the average response time is 7-10 business days to receive the results.
Lipomic LifeSciences can provide evidence-based suggestions for lifestyle changes that you can make to positively impact your health. We can also connect you with leading medical experts who can guide and discuss potential next steps.
Test Specific FAQs
The word ‘inflammation’ comes from the Latin word “inflammare” which means ‘to set on fire’. Traditionally, one associates inflammation with the four cardinal signs – redness, swelling, heat and pain. This is what is known as the classical “acute inflammation”. This happens in response to an injury or an infection by a foreign agent like bacteria, virus, fungus, parasites etc. The body’s defence mechanism is activated and cells and molecules reach the site of injury/infection in order to eliminate the offending agents. Thus, inflammation is necessary to control infections, heal wounds and clear injured tissues and festering sores. Generally, inflammation subsides after the aforementioned goals are achieved. What happens however, when the body’s response does not subside and may not even be against any particular target? That is what is known as chronic inflammation. By definition, chronic inflammation is a response of prolonged duration (weeks or months). Causes of chronic inflammation can include persistent infections, hypersensitivity diseases, prolonged exposure to toxic agents etc. Research now links chronic inflammation with stress, poor lifestyle choices and dietary patterns. If left unchecked, prolonged chronic inflammation starts affecting and attacking healthy cells. Chronic inflammation creates a microenvironment suitable to the development of several complex diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, auto-immune diseases.
C-Reactive Protein or CRP is a protein produced primarily by the liver in response to inflammation. The levels of CRP increase up to a 1000 fold at the site of infection or injury.2 CRP has traditionally been used as a marker for infection and cardiovascular diseases.3 Baseline CRP levels can vary according to age, gender, smoking status, weight, lipid levels, and blood pressure but for a standard CRP test, a normal reading is less than 6 milligram per liter (mg/L). A test result showing a CRP level greater than 6 mg/L should be further investigated by a medical practitioner.
The test results will indicate whether your CRP levels are in the reference range. CRP is a non specific marker of inflammation and might be temporarily elevated due to a recent infection, illness or trauma and it is recommended that you repeat the CRP test after a month. If your levels are elevated after the retest too, you must share your results with your healthcare provider and discuss potential steps.
Chronic Inflammation is related to a myriad of health problems, as represented in the diagram below:

Source: Fighting Inflammation, Harvard Special Health Report
Sample Report











